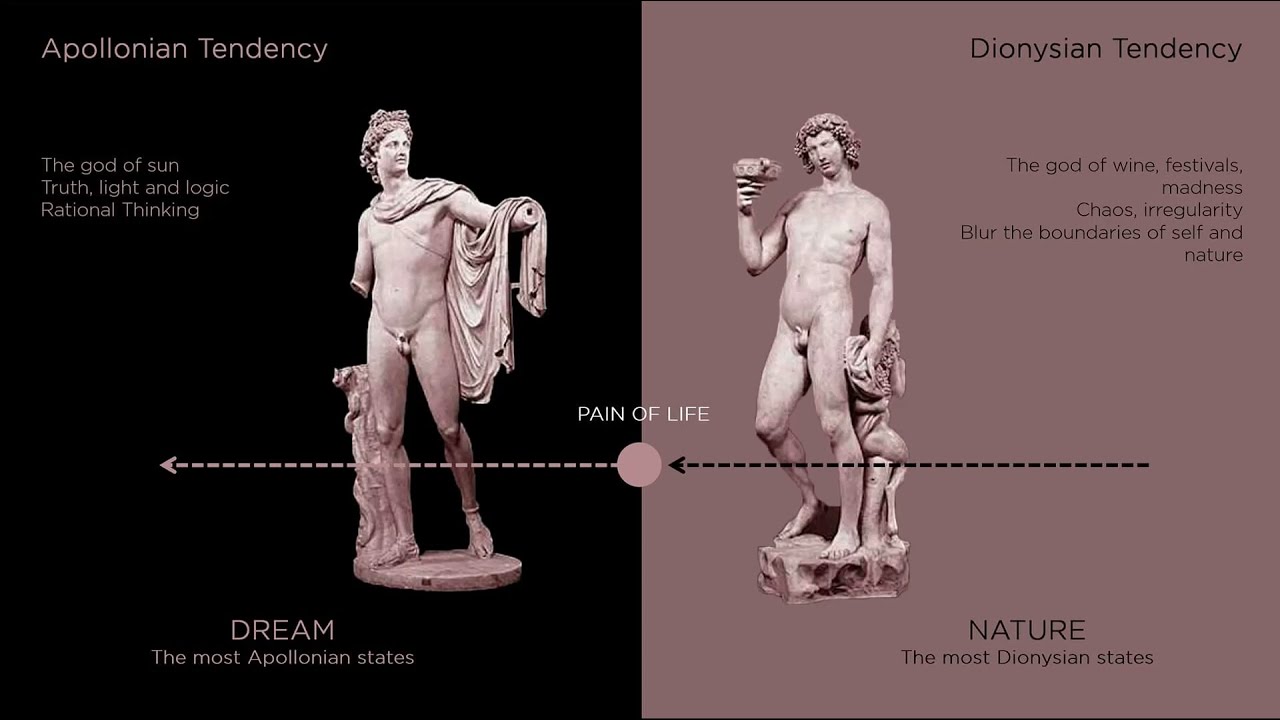
In the annals of Western philosophy, Dionysianism stands as a captivating and enigmatic concept, embodying a primal force that urges us to explore the depths of our existence. Rooted in ancient Greek mythology and later immortalized by Friedrich Nietzsche, Dionysianism offers a profound perspective on human nature, creativity, and the pursuit of ecstasy. As we delve into its essence, we uncover a philosophy that celebrates spontaneity, chaos, and the intoxicating allure of life’s mysteries.
Originating from the cult of Dionysus, the Greek god of wine, ecstasy, and revelry, Dionysianism emerges as a stark contrast to its Apollonian counterpart. Where Apollo represents order, reason, and rationality, Dionysus embodies chaos, passion, and instinctual urges. This duality forms the basis of Nietzsche’s exploration in his seminal work, “The Birth of Tragedy.” Nietzsche posits that within the realm of art and culture, these opposing forces intertwine to create sublime experiences, particularly in Greek tragedy.
At the heart of Dionysianism lies the notion of ecstatic release—a transcendent state of being where individuals abandon societal norms and embrace their primal instincts. Dionysian rituals, often accompanied by music, dance, and intoxication, serve as avenues for individuals to commune with the divine and tap into the raw vitality of existence. In the throes of ecstasy, distinctions between self and other blur, giving rise to a collective sense of euphoria and unity.
In Nietzschean philosophy, the Dionysian spirit finds expression not only in artistic endeavors but also in the pursuit of individual authenticity. Nietzsche champions the “will to power,” a driving force within every individual that seeks self-overcoming and self-expression. Embracing one’s Dionysian impulses entails confronting the chaos within and harnessing it to forge a more vibrant and authentic existence.
The Dionysian ethos reverberates through various facets of human experience, from artistic creation to the realm of emotions and desires. In art, the Dionysian impulse manifests in works that evoke intense emotional responses, transcending rational comprehension. Greek tragedies, with their exploration of suffering, fate, and the human condition, epitomize this fusion of chaos and beauty.
Moreover, Dionysianism challenges conventional morality and societal norms, inviting individuals to confront the taboo and the forbidden. It embraces the shadow aspects of human nature—the irrational, the instinctual, and the dark—as essential components of the human psyche. By embracing these aspects rather than repressing them, individuals can attain a deeper understanding of themselves and the world around them.
In contemporary society, the Dionysian spirit finds expression in various cultural movements and subcultures that celebrate freedom, hedonism, and nonconformity. From the countercultural revolution of the 1960s to the rave culture of the 1990s and beyond, Dionysian impulses continue to influence art, music, and lifestyle choices. These movements serve as reminders of the enduring appeal of ecstatic experiences and the human yearning for transcendence.
However, the Dionysian path is not without its pitfalls. Excessive indulgence in hedonism and the pursuit of pleasure can lead to nihilism and self-destruction. Nietzsche warns against succumbing to the passive, hedonistic aspects of Dionysianism, advocating instead for a more active engagement with life’s challenges and contradictions. True liberation, according to Nietzsche, arises not from mere hedonism but from the disciplined affirmation of life in all its complexities.
Moreover, the tension between the Dionysian and Apollonian forces highlights the delicate balance between chaos and order, spontaneity and structure. While the Dionysian impulse encourages freedom and creativity, the Apollonian principle provides the necessary scaffolding for artistic expression and cultural coherence. It is in the dynamic interplay between these opposing forces that the richness of human experience unfolds.
Conclusion
Dionysianism offers a compelling perspective on the human condition—one that celebrates the chaotic, the irrational, and the ecstatic aspects of existence. Rooted in ancient mythology and revitalized by Nietzschean philosophy, Dionysianism invites individuals to embrace their primal instincts, confront their inner demons, and forge a deeper connection with life’s mysteries. Whether through art, culture, or personal transformation, the Dionysian spirit continues to inspire seekers of truth and authenticity, beckoning them to explore the wild depths of human experience.