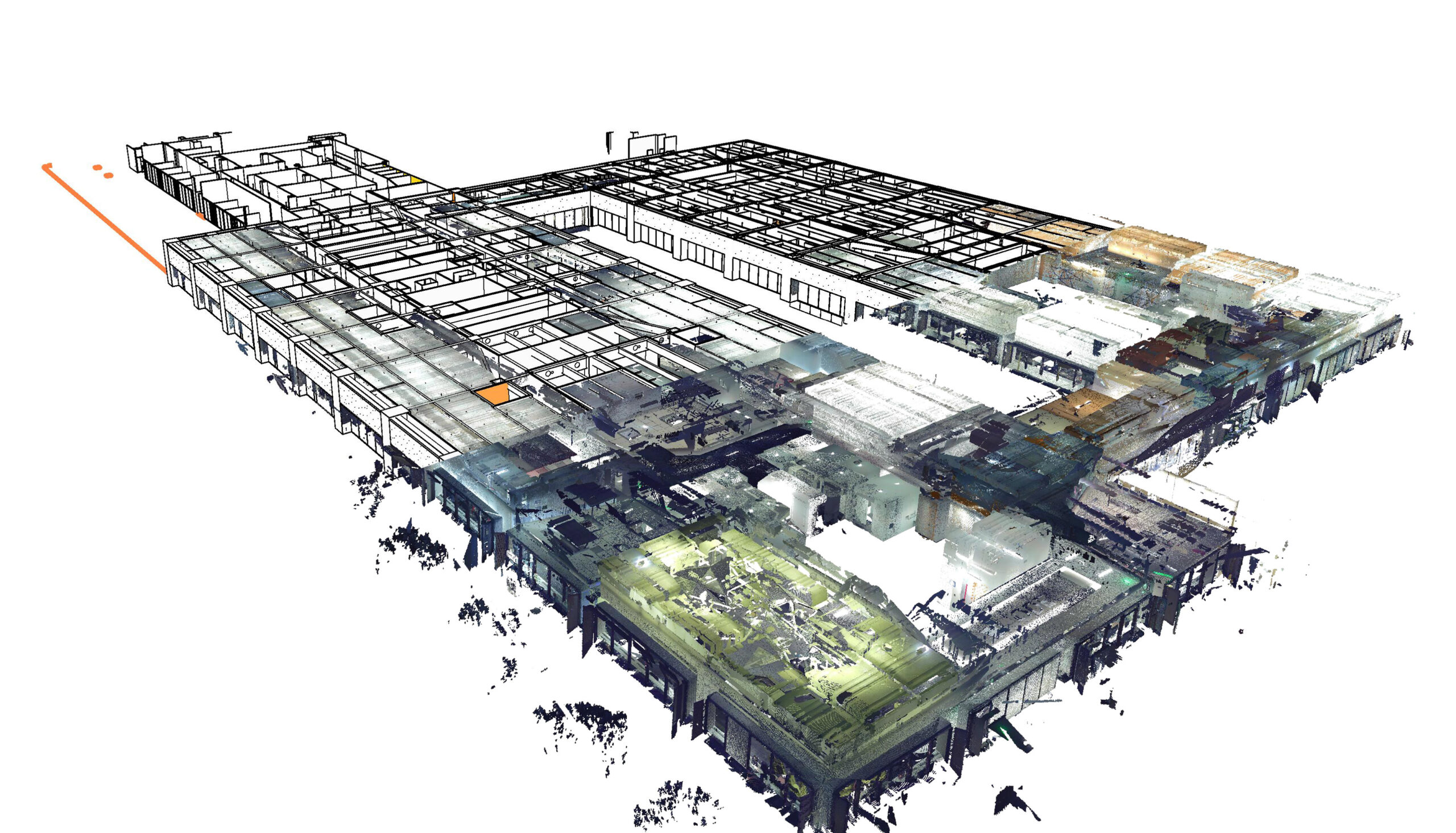
In the ever-evolving world of construction and architecture, technology continues to revolutionize the way we design, plan, and build. One such groundbreaking technology is Scan to BIM, a process that transforms real-world structures captured as point clouds into accurate and detailed virtual models. This blog will delve into the Scan to BIM modeling, exploring its benefits, the steps involved, and its impact on the construction industry.
Understanding Point Clouds:
Point clouds are vast sets of data points generated by 3D laser scanning devices, such as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging). These scans capture millions of points on the surface of an object or structure, creating a highly accurate representation of its physical geometry.
Importance of Scan to BIM:
The Scan to BIM process plays a crucial role in construction and architectural projects. By converting point cloud data into Building Information Models (BIM), professionals gain access to a digital representation that offers more insights and opportunities throughout the project lifecycle.
Advantages of Scan to BIM:
Accuracy and Precision
Scan to BIM eliminates manual measurement errors and provides unparalleled accuracy in capturing as-built conditions. The resulting virtual model represents the real-world structure with precision, facilitating informed decision-making.
Time and Cost Efficiency
Traditional as-built surveys are time-consuming and labor-intensive. Scan to BIM expedites the data collection process and significantly reduces the overall project timeline. Moreover, the early detection of clashes and discrepancies in the virtual model saves costs that would otherwise arise during construction.
Enhanced Collaboration
BIM models serve as a collaborative platform for various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. The 3D visualization of the project fosters better communication and coordination among team members.
Clash Detection and Risk Mitigation
Scan to BIM enables clash detection analysis, identifying potential conflicts between different building systems and components. Addressing these issues before construction mitigates risks and minimizes costly rework.
The Scan to BIM Process
3D Laser Scanning
The process commences with 3D laser scanning, where specialized equipment captures the physical structure’s point cloud data. This data includes geometric details, such as walls, floors, columns, and intricate architectural elements.
Point Cloud Registration
Multiple scans are often necessary to capture entire structures. Point cloud registration combines these individual scans into a unified coordinate system, creating a comprehensive representation of the building.
Data Cleanup and Filtering
Raw point cloud data can be noisy and contain unwanted artifacts. Data cleanup and filtering techniques remove redundant or erroneous points, ensuring the final model is accurate and reliable.
Point Cloud to Mesh Conversion
The point cloud is converted into a mesh, which represents the surfaces of the captured objects. This conversion allows for easier manipulation and visualization of the structure.
Model Generation in BIM Software
The mesh data is imported into BIM software, where the actual modeling process takes place. Building elements such as walls, floors, doors, and windows are created, using the mesh as a reference.
Adding Metadata
BIM models go beyond geometric representation; they also contain metadata about the building components. This information includes material specifications, manufacturer details, installation dates, and maintenance schedules.
Revit Families and Object Libraries
To improve efficiency, pre-built Revit families and object libraries can be utilized. These resources offer a wide range of components that match real-world products, ensuring accuracy in the virtual model.
Quality Control and Validation
The completed BIM model undergoes rigorous quality control and validation processes. Checking for accuracy and adherence to standards is vital before proceeding to the construction phase.
Applications of Scan to BIM:
Renovation and Retrofitting
In renovation projects, Scan to BIM aids in assessing existing structures, identifying areas that need attention, and designing suitable modifications.
Historic Preservation
Preserving historical buildings demands precision and care. Scan to BIM helps document and restore these structures without causing any damage to their original features.
Facility Management
BIM models facilitate efficient facility management, enabling easy access to critical information about building components, maintenance schedules, and asset tracking.
Conclusion
Scan to BIM represents a paradigm shift in the construction industry, harnessing cutting-edge technology to transform real-world structures into virtual models. The process empowers professionals with accurate data, streamlined collaboration, and better decision-making capabilities.
Also Read: The Art of Turning Point Cloud Data into Intelligent BIM Models